Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia Due to MRSA vs. MSSA: What Should Guide Empiric Therapy?
Can we use nasal swab to guide empiric antibiotic therapy in ventilator-associated pneumonia? See the results from the retrospective analysis of more than 1400 patients in our ICU.
Free full text here on Antibiotics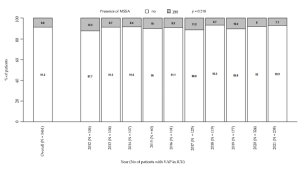
Abstract
The guidelines on ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) recommend an empiric therapy against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) according to its prevalence rate. Considering the MRSA and MSSA VAP prevalence over the last 9 years in our tertiary care hospital, we assessed the clinical value of the MRSA nasal-swab screening in either predicting or ruling out MRSA VAP. We extracted the data of 1461 patients with positive bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL). Regarding the MRSA nasal-swab screening, 170 patients were positive for MRSA or MSSA. Overall, MRSA had a high prevalence in our ICU. Despite the COVID-19 pandemic, there was a significant downward trend in MRSA prevalence, while MSSA remained steady over time. Having VAP due to MRSA did not have any impact on LOS and mortality. Finally, the MRSA nasal-swab testing demonstrated a very high negative predictive value for MRSA VAP. Our results suggested the potential value of a patient-centered approach to improve antibiotic stewardship.