Grip
every-day activities
Sharing
Our philosophy
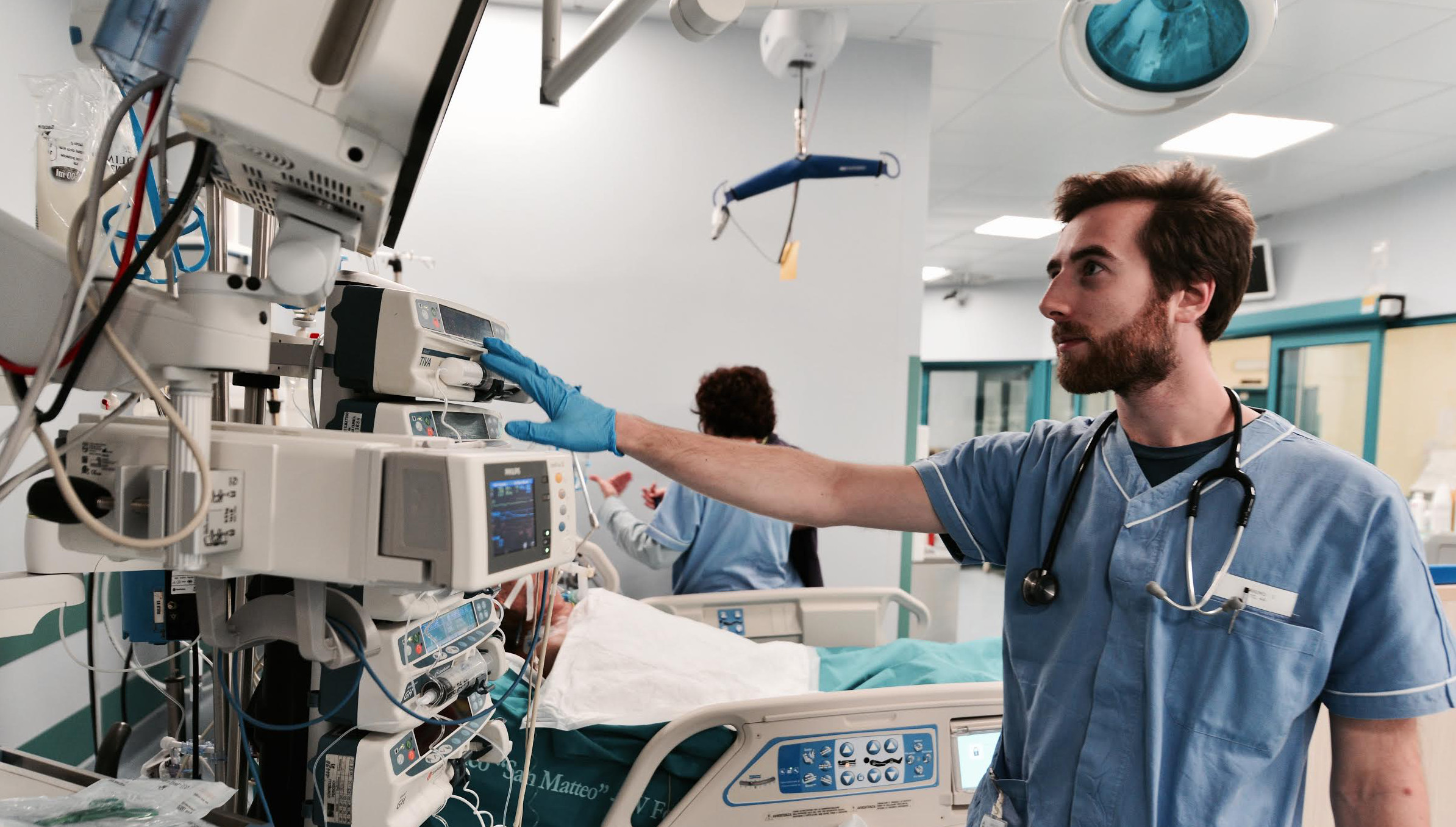
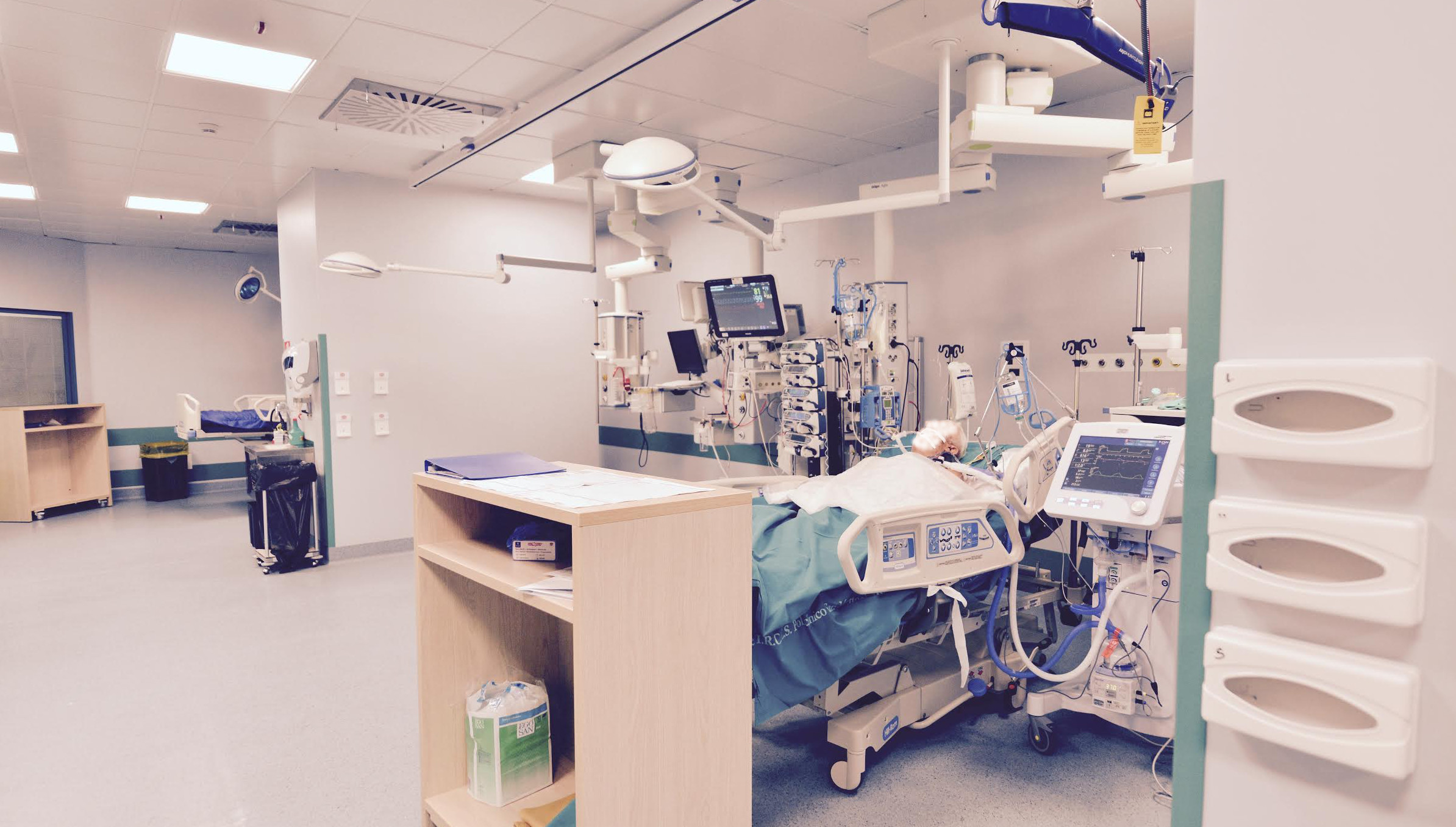
The GRIP (Group for Research in Intensive care in Pavia) is founded in 2015 by a group of intensivists working at Intensive Care Units of Policlinico S. Matteo in Pavia. We are a group of young doctors and researchers who dedicated in the last years great energy, enthusiasm and time to develop new ideas, improve technology and optimize quality of care for critical patients. Our group is characterized by strong international connections for both clinical research and technological developement. Our missions are:
-
1Innovation
Intensive care units are highly technological; therefore, development of innovative instruments and optimization of existing ones can have a deep clinical impact. We have strong national and international collaborations with research and development sections of industries involved in the field and with many universities in order to push technology forward.
-
2Grip
Our aim is to promote and support a research projects gripping the real world. First, this means we support research with high clinical impact and strong everyday applicability. Second, we support researchers, offering work possibilities for young professionals.
-
3Sharing
We aim to share our ideas, projects and results with scientific community; we have strong national and international research cooperation and researcher exchange programs with multiple university centers.
The mental health toll of COVID-19: significant increase in admissions to ICU for voluntary self-inflicted injuries after the beginning of the pandemic
 The GRIP
The GRIP